You have a project?
Ask questions about Lascom products to our team of experts; we will be glad to answer you as soon as possible. Express your needs and expectations; we will do our best to organize a meeting with our sales team.
Food regulations are continually evolving with significant differences from one country to another, impacting each and every department of a company. In fact, those regulations impact every step of a product development, from R&D to marketing through procurement and quality. Non-conformity in product composition, labeling or claims can be both costly and damaging to a brand image.
To ensure an efficient product development with a fast go-to-market for targeted countries, it is essential to set up and follow regulatory frameworks to comply to local rules all along the product life cycle . It requires an international network of regulatory experts in order to share structured information, ensure data continuity from suppliers to consumers, and elaborate an efficient collaboration facilitated by optimized processes.
The authorization of an ingredient or additive is strictly connected to the finished product’s legal name, so it is recommended to properly define the product category in order to assess if the ingredients, including additives, are allowed in this specific category. In the US, manufacturers have to follow standards that may vary from one state to another. For instance, the California Proposition 65 (CA PROP 65), administered by the Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment (OEHHA) of the California Environmental Protection Agency (CalEPA), determines whether chemicals meet the criteria to be added to the CA PROP 65 list, and administers labeling, warning and risk exposure requirements for these substances to be placed on the Californian market. This law is intended to protect citizens from a list of chemicals that are known to cause cancer, birth defects or other reproductive harm. Recently, the Proposition 65 was enforced, when a California judge ruled that coffee must carry a cancer warning under the state law known as Proposition 65.
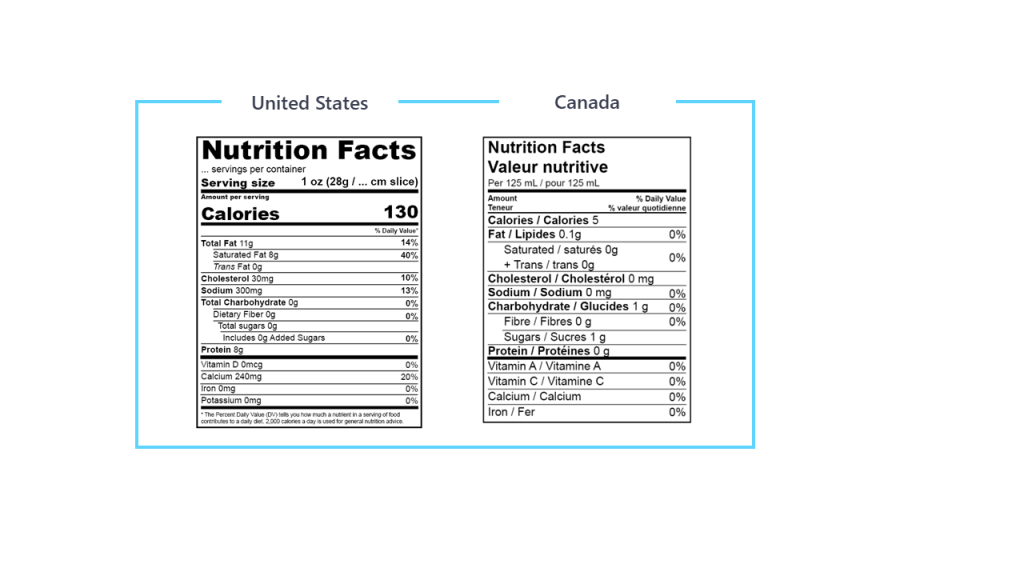
In the US, the Code of Federal Regulations covers almost all requirements regarding nutritional labeling, food additives, and product standards. It also covers the new Nutrition Facts Label requirements.
In Canada, Health Canada is responsible to set out policies, regulations and standards for food and nutrition labeling, food additives, advertising and product standards under the Food and Drugs Act. It also includes requirements for the Nutrition Facts table.
 Packaging eco-design
Packaging eco-designLike labeling, packaging can also be subject to regulations that differ from one country to another. In Europe, the Packaging Directive 94/62/EC legislation set targets that each country needs to meet with their own strategy and legislation. Therefore, regulatory texts can differ among the European countries. For instance, in Germany, on January 1, 2019, a new Packaging Act will introduce additional ecological waste management requirements. Food and beverage manufacturers will need to set up a collection and disposal system to manage one-way packaging placed on the market for “private consumers”.
Food Contact Materials (FCMs) are materials which are or are intended to be in contact with food during its production, processing, storage, preparation and serving. Thus, they can have an impact on food safety and quality throughout the entire supply chain. Again, FCMs are handled differently from one country to another. In the US, the FDA is in charge of the risk assessment and management of the FCMs. Each individual substance that comprises an article dictates the overall regulatory status of a food contact material. These individual substances should be covered by one of the following:
Food and beverage manufacturers are likely to face two main challenges when dealing with food regulations:
